.
Nomad
A flexible workload orchestrator that enables an organization to easily deploy and manage containerized or legacy applications

🚀 Introduction
HashiCorp Nomad is a highly available, distributed, data-center aware cluster and application scheduler designed to support the modern datacenter. In this HashiQube DevOps lab, you'll get hands-on experience working with Nomad.
Teams increasingly want to move away from the traditional tight coupling of application and operating system. They need an abstraction layer to help developers and operators work together, and save money with better hardware utilization. HashiCorp Nomad meets this need by providing a flexible workload orchestrator.
📰 Latest News
- Nomad 1.7 beta improves Vault and Consul integrations, adds NUMA support
- Nomad 1.6 adds node pools, UX updates, and more
- Nomad 1.5 adds single sign-on and dynamic node metadata
- Nomad 1.4 Adds Nomad Variables and Updates Service Discovery
- Nomad 1.3 Adds Native Service Discovery and Edge Workload Support
🛠️ Provision
Choose one of the following methods to set up your environment:
vagrant up --provision-with basetools,docker,docsify,consul,nomaddocker compose exec hashiqube /bin/bash
bash hashiqube/basetools.sh
bash docker/docker.sh
bash consul/consul.sh
bash nomad/nomad.shAfter provisioning, you will have access to the Nomad UI:
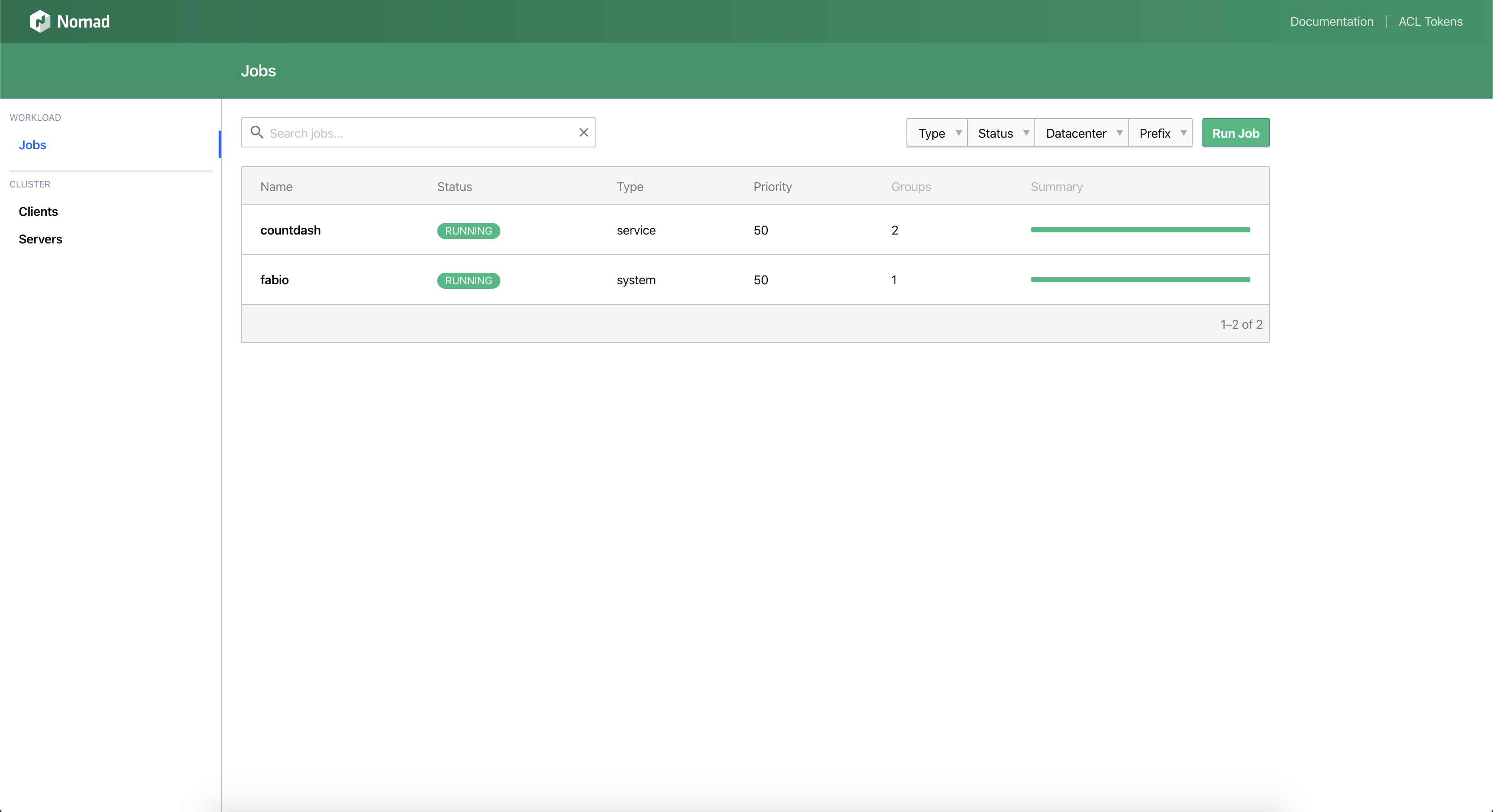
🧩 Nomad Provisioner
The nomad.sh script handles the installation and configuration of Nomad:
# Nomad provisioning script content
[filename](nomad.sh ':include :type=code')📊 Monitoring Nomad
We use Prometheus and Grafana to monitor Nomad deployments.
💡 For more information, see: Monitoring Hashicorp Nomad
🔄 Traefik on Nomad

Traefik Proxy now fully integrates with the new Nomad built-in Service Discovery. This first-of-its-kind ingress integration simplifies ingress in HashiCorp Nomad, making it easier than ever to utilize Nomad directly with Traefik Proxy.
Before Nomad 1.3, when using service discovery with Nomad, Traefik Proxy users had to use Hashicorp Consul and Nomad side-by-side to benefit from Traefik Proxy's automatic configuration. Now, Nomad has a simple and straightforward built-in service discovery, improving usability in both test environments and edge deployments.
Access Traefik
- Dashboard:
http://localhost:8181 - Load Balancer:
http://localhost:8080/
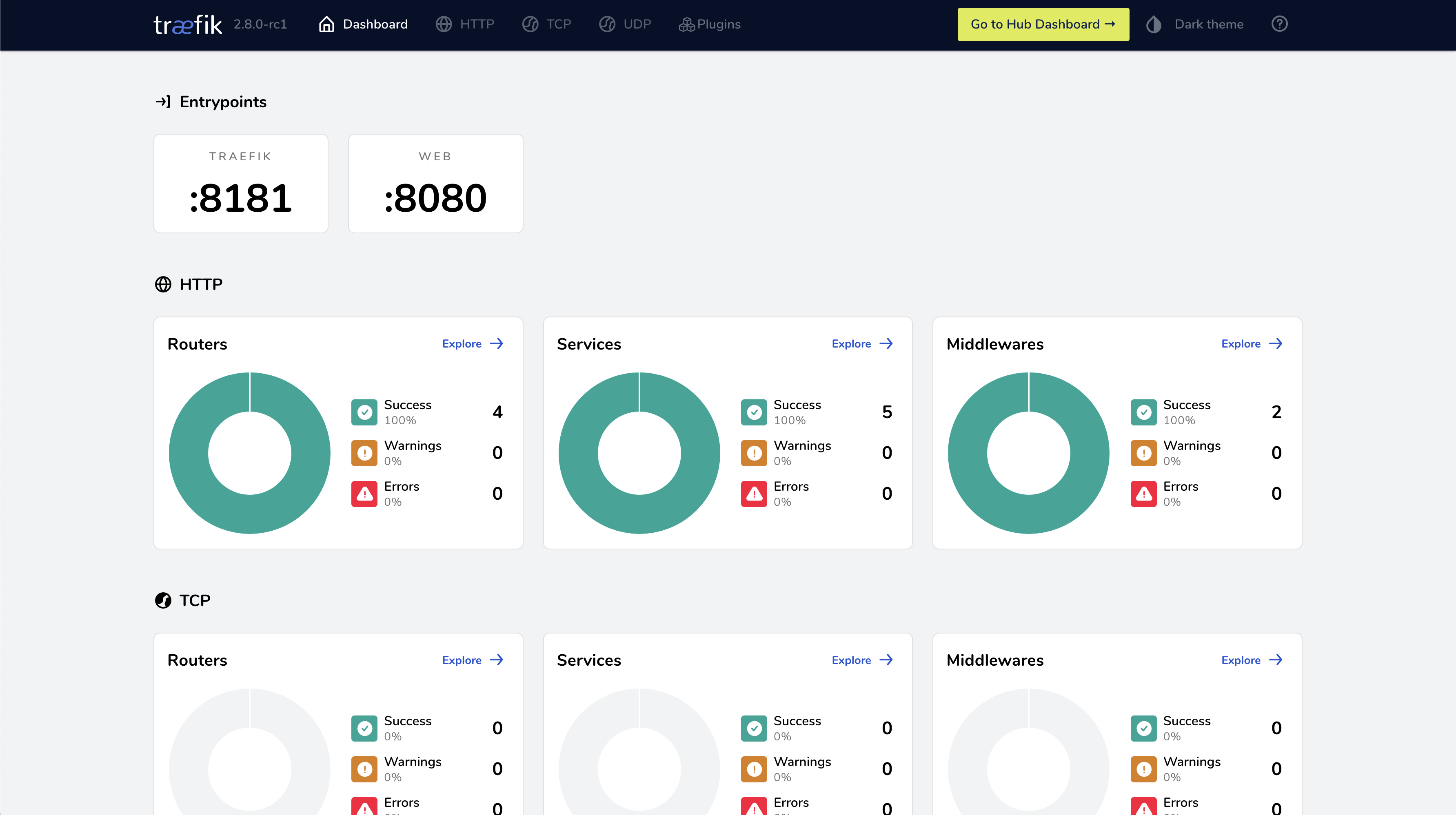
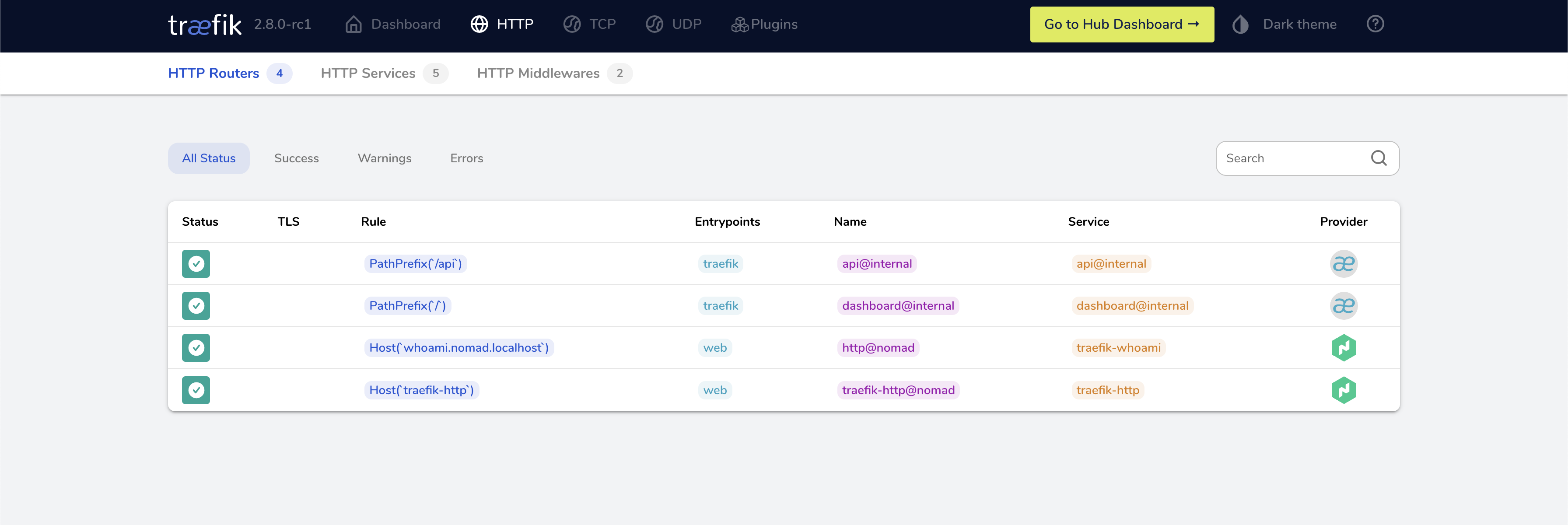
Traefik Nomad Job Configuration
# Traefik job configuration
[filename](nomad/jobs/traefik.nomad ':include :type=code hcl')Testing the Traefik Configuration
The native Service Discovery in Nomad works seamlessly with Traefik. To test it:
curl -H "Host: whoami.nomad.localhost" http://localhost:8080 -vSample output:
* Trying 127.0.0.1:8080...
* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 8080 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: whoami.nomad.localhost
> User-Agent: curl/7.79.1
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 365
< Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< Date: Thu, 16 Jun 2022 02:08:56 GMT
<
Hostname: 86bb7e3d366a
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: 172.18.0.5
RemoteAddr: 172.18.0.1:51192
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: whoami.nomad.localhost
User-Agent: curl/7.79.1
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip
X-Forwarded-For: 172.17.0.1
X-Forwarded-Host: whoami.nomad.localhost
X-Forwarded-Port: 80
X-Forwarded-Proto: http
X-Forwarded-Server: 5d7dc64220c8
X-Real-Ip: 172.17.0.1
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intactTraefik Whoami Example Job
# Traefik whoami job configuration
[filename](nomad/jobs/traefik-whoami.nomad ':include :type=code hcl')🌐 Fabio on Nomad
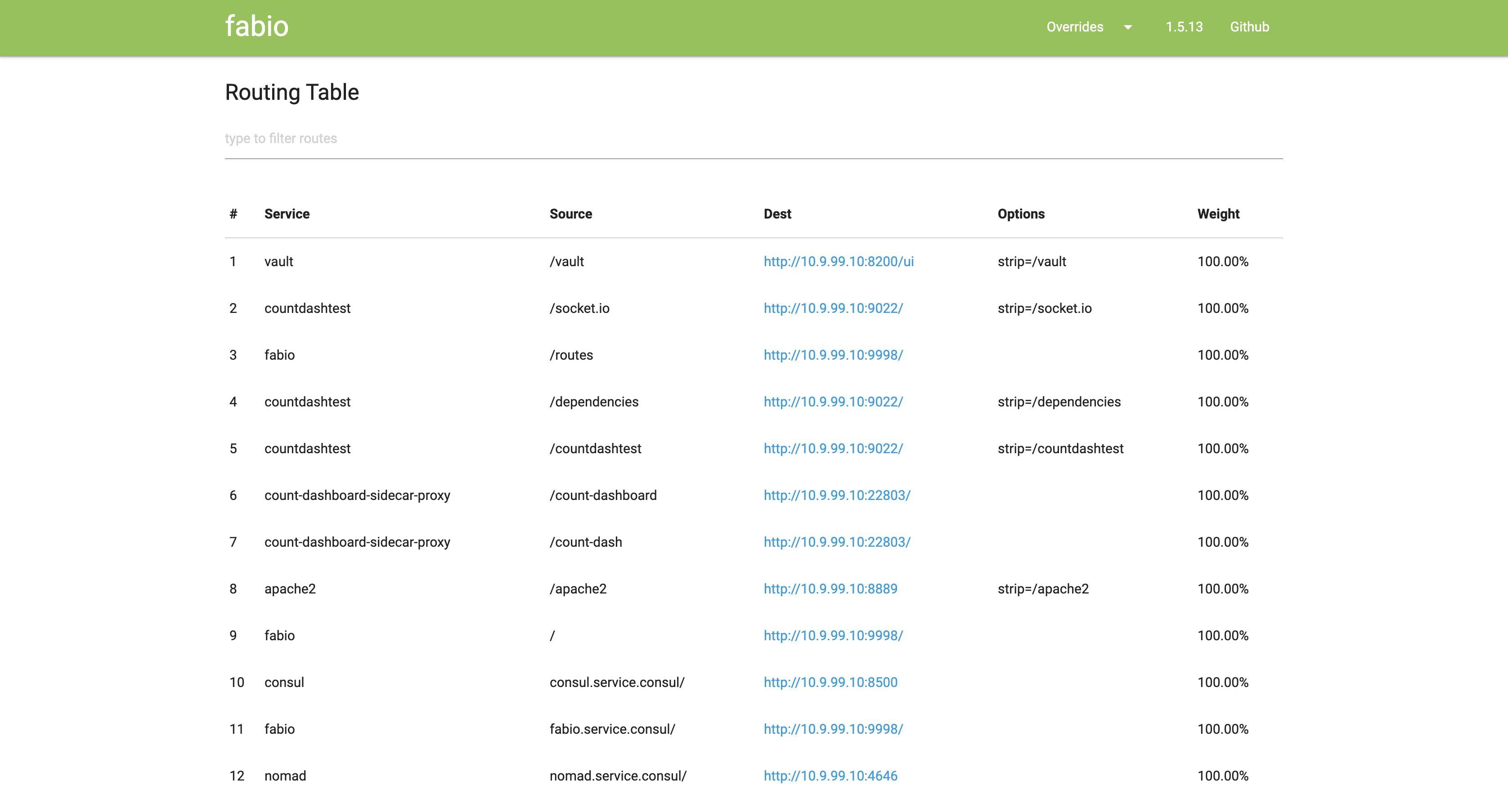
Fabio is an HTTP and TCP reverse proxy that configures itself with data from Consul.
Unlike traditional load balancers and reverse proxies that require manual configuration files, Fabio updates its routing table directly from the data stored in Consul as soon as there is a change, without requiring restart or reloading.
When you register a service in Consul, simply add a tag that announces the paths the upstream service accepts (e.g., urlprefix-/user or urlprefix-/order), and Fabio will do the rest.
Access Fabio
- Load Balancer:
http://localhost:9999/ - UI:
http://localhost:9998
Fabio Nomad Job Configuration
# Fabio job configuration
[filename](nomad/jobs/fabio.nomad ':include :type=code hcl')Fabio Properties Configuration
# Fabio properties configuration
[filename](nomad/jobs/fabio.properties ':include :type=code config')📚 Resources
- Nomad Official Website
- Traefik Proxy and Nomad Integration
- Traefik Nomad Provider Documentation
- Fabio GitHub Repository
#!/bin/bash
VERSION=latest
arch=$(lscpu | grep "Architecture" | awk '{print $NF}')
if [[ $arch == x86_64* ]]; then
ARCH="amd64"
elif [[ $arch == aarch64 ]]; then
ARCH="arm64"
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"CPU is $ARCH"
# https://github.com/hashicorp/nomad/issues/19343 nomad needs dmidecode
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get --assume-yes install -qq dmidecode curl unzip jq < /dev/null > /dev/null
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Cleanup any Nomad if found"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo systemctl stop nomad
sudo rm -rf /etc/nomad
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/nomad
sudo rm -rf /opt/nomad
sudo rm -rf /tmp/nomad.zip
sudo rm -rf /opt/cni
sudo rm -rf /tmp/cni-plugins.tgz
yes | sudo docker system prune -a
yes | sudo docker system prune --volumes
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Consul is running (Dependency)"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if pgrep -x "consul" >/dev/null
then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Consul is running"
else
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Consul is running.."
sudo bash /vagrant/consul/consul.sh
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Docker Daemon is running (Dependency)"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if pgrep -x "dockerd" >/dev/null
then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Docker is running"
else
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Docker is running.."
sudo bash /vagrant/docker/docker.sh
fi
if [ -f /vagrant/nomad/license.hclic ]; then
# https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/tutorials/enterprise/hashicorp-enterprise-license
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Found license.hclic Installing Enterprise Edition version: $VERSION"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
export NOMAD_LICENSE_PATH=/vagrant/nomad/license.hclic
export NOMAD_LICENSE=$(cat /vagrant/nomad/license.hclic)
if [[ $VERSION == "latest" ]]; then
LATEST_URL=$(curl -sL https://releases.hashicorp.com/nomad/index.json | jq -r '.versions[].builds[].url' | sort -t. -k 1,1n -k 2,2n -k 3,3n -k 4,4n | egrep 'ent' | egrep "linux.*$ARCH" | sort -V | tail -n 1)
else
LATEST_URL=$(curl -sL https://releases.hashicorp.com/nomad/index.json | jq -r '.versions[].builds[].url' | sort -t. -k 1,1n -k 2,2n -k 3,3n -k 4,4n | egrep 'ent' | egrep "linux.*$ARCH" | sort -V | grep $VERSION | tail -1)
fi
else
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing Community Edition version: $VERSION"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if [[ $VERSION == "latest" ]]; then
LATEST_URL=$(curl -sL https://releases.hashicorp.com/nomad/index.json | jq -r '.versions[].builds[].url' | sort -t. -k 1,1n -k 2,2n -k 3,3n -k 4,4n | egrep -v 'rc|ent|beta' | egrep "linux.*$ARCH" | sort -V | tail -n 1)
else
LATEST_URL=$(curl -sL https://releases.hashicorp.com/nomad/index.json | jq -r '.versions[].builds[].url' | sort -t. -k 1,1n -k 2,2n -k 3,3n -k 4,4n | egrep -v 'rc|ent|beta' | egrep "linux.*$ARCH" | sort -V | grep $VERSION | tail -1)
fi
fi
wget -q $LATEST_URL -O /tmp/nomad.zip
mkdir -p /usr/local/bin
(cd /usr/local/bin && unzip -o /tmp/nomad.zip)
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installed `/usr/local/bin/nomad --version`"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# create /var/log/nomad.log
sudo touch /var/log/nomad.log
# create Nomad data directories
sudo mkdir -p /etc/nomad
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Create Nomad Systemd service file"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# create a Nomad service file at /etc/systemd/system/nomad.service
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/nomad.service
[Unit]
Description=Nomad
Documentation=https://nomadproject.io/docs/
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
# When using Nomad with Consul it is not necessary to start Consul first. These
# lines start Consul before Nomad as an optimization to avoid Nomad logging
# that Consul is unavailable at startup.
#Wants=consul.service
#After=consul.service
[Service]
# EnvironmentFile=/etc/nomad.d/nomad.env
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/nomad agent -config=/etc/nomad/server.conf -dev-connect
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
LimitNOFILE=65536
LimitNPROC=infinity
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=2
LogsDirectory=nomad
StandardOutput=append:/var/log/nomad.log
StandardError=append:/var/log/nomad.log
StartLimitBurst=3
## Configure unit start rate limiting. Units which are started more than
## *burst* times within an *interval* time span are not permitted to start any
## more. Use StartLimitIntervalSec or StartLimitInterval (depending on
## systemd version) to configure the checking interval and StartLimitBurst
## to configure how many starts per interval are allowed. The values in the
## commented lines are defaults.
TasksMax=infinity
OOMScoreAdjust=-1000
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Create Nomad config file /etc/nomad/server.conf"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/nomad/server.conf
data_dir = "/var/lib/nomad"
bind_addr = "0.0.0.0" # the default
datacenter = "dc1"
advertise {
# Defaults to the first private IP address.
http = "{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}"
rpc = "{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}"
serf = "{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}:5648" # non-default ports may be specified
}
server {
enabled = true
bootstrap_expect = 1
}
autopilot {
cleanup_dead_servers = true
last_contact_threshold = "400ms"
max_trailing_logs = 250
server_stabilization_time = "30s"
enable_redundancy_zones = false
disable_upgrade_migration = false
enable_custom_upgrades = false
}
client {
enabled = true
# https://github.com/hashicorp/nomad/issues/1282
network_speed = 100
# https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/docs/configuration/client#cpu_total_compute
# BUG: CPU fingerprint with Docker Desktop on Apple Silicon never really worked because the CPU speed is not made available anywhere, so its impossible for Nomad to detect it
# If you run previous versions of Nomad you will notice that the fingerprinted capacity is always 1000MHz. This is a value we used to hardcode as a fallback but we dont anymore on 1.7.x (https://github.com/hashicorp/nomad/blob/release/1.6.x/client/fingerprint/cpu.go#L23) because its just wrong.
# The only option for now is to pass their own hardcoded value using client.cpu_total_compute (https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/docs/configuration/client#cpu_total_compute)
cpu_total_compute = 8000
servers = ["{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}:4647"]
# network_interface = "enp0s8"
# https://www.nomadproject.io/docs/drivers/docker.html#volumes
# https://github.com/hashicorp/nomad/issues/5562
options = {
"docker.volumes.enabled" = true
"docker.auth.config" = "/etc/docker/auth.json"
}
host_volume "waypoint" {
path = "/opt/nomad/data/volume/waypoint"
read_only = false
}
}
plugin "docker" {
config {
endpoint = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
volumes {
enabled = true
selinuxlabel = "z"
}
allow_privileged = true
allow_caps = ["chown", "net_raw"]
}
}
plugin "raw_exec" {
config {
enabled = true
}
}
# https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/docs/configuration/telemetry
# https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/docs/configuration/telemetry#prometheus
# https://developer.hashicorp.com/nomad/docs/operations/monitoring-nomad
telemetry {
collection_interval = "1s"
disable_hostname = true
prometheus_metrics = true
publish_allocation_metrics = true
publish_node_metrics = true
}
consul {
address = "{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}:8500"
}
EOF
if [ -f /vagrant/nomad/license.hclic ]; then
sed -i -e 's;bootstrap_expect = 1;bootstrap_expect = 1\n license_path = "/vagrant/nomad/license.hclic";' /etc/nomad/server.conf
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Creating Waypoint host volume /opt/nomad/data/volume/waypoint"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo mkdir -p /opt/nomad/data/volume/waypoint
sudo chmod -R 777 /opt/nomad
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Check if CNI Plugins are installed"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if [ -f /opt/cni/bin/bridge ]; then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ CNI Plugins already installed"
else
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ CNI Plugins not found, installing.."
wget -q https://github.com/containernetworking/plugins/releases/download/v1.4.1/cni-plugins-linux-$ARCH-v1.4.1.tgz -O /tmp/cni-plugins.tgz
mkdir -p /opt/cni/bin
tar -C /opt/cni/bin -xzf /tmp/cni-plugins.tgz
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-arptables
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-ip6tables
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
fi
# start and enable nomad service to start on system boot
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Start Nomad Service"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo service nomad start
sh -c 'sudo tail -f /var/log/nomad.log | { sed "/node registration complete/ q" && kill $$ ;}'
sleep 2
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Get Nomad Members and Status"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sleep 10
nomad server members
nomad node status
cd /vagrant/nomad/nomad/jobs;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Start Nomad Fabio job"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
nomad plan --address=http://localhost:4646 fabio.nomad
nomad run --address=http://localhost:4646 fabio.nomad
# # curl -v -H 'Host: fabio.service.consul' http://${VAGRANT_IP}:9999/
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Start Nomad Traefik job"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
nomad plan --address=http://localhost:4646 traefik.nomad
nomad run --address=http://localhost:4646 traefik.nomad
# nomad plan --address=http://localhost:4646 traefik-whoami.nomad
# nomad run --address=http://localhost:4646 traefik-whoami.nomad
if [ -f /vagrant/nomad/license.hclic ]; then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Nomad License Inspect"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
nomad license inspect /vagrant/nomad/license.hclic
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Access Nomad"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Nomad http://localhost:4646"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Nomad Documentation http://localhost:3333/#/nomad/README?id=nomad"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Fabio Dashboard http://localhost:9998"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Fabio Loadbalancer http://localhost:9998"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Fabio Documentation http://localhost:3333/#/nomad/README?id=fabio-load-balancer-for-nomad"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Treafik Dashboard http://localhost:38081"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Traefik Loadbalancer: http://localhost:38080"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Traefik Documentation: http://localhost:3333/#/nomad/README?id=traefik-load-balancer-for-nomad"