.
Minikube
Run a single-node Kubernetes cluster for local development and learning
🚀 Introduction
Minikube is a tool that runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster in a virtual machine on your personal computer. This HashiQube DevOps lab provides hands-on experience with Minikube, Helm, Helm Dashboard, and Traefik, allowing you to learn and experiment with Kubernetes in a safe, local environment.
🛠️ Provision
Choose one of the following methods to provision your environment:
vagrant up --provision-with basetools,docker,docsify,minikubedocker compose exec hashiqube /bin/bash
bash hashiqube/basetools.sh
bash docker/docker.sh
bash docsify/docsify.sh
bash minikube/minikube.sh📊 Key Components
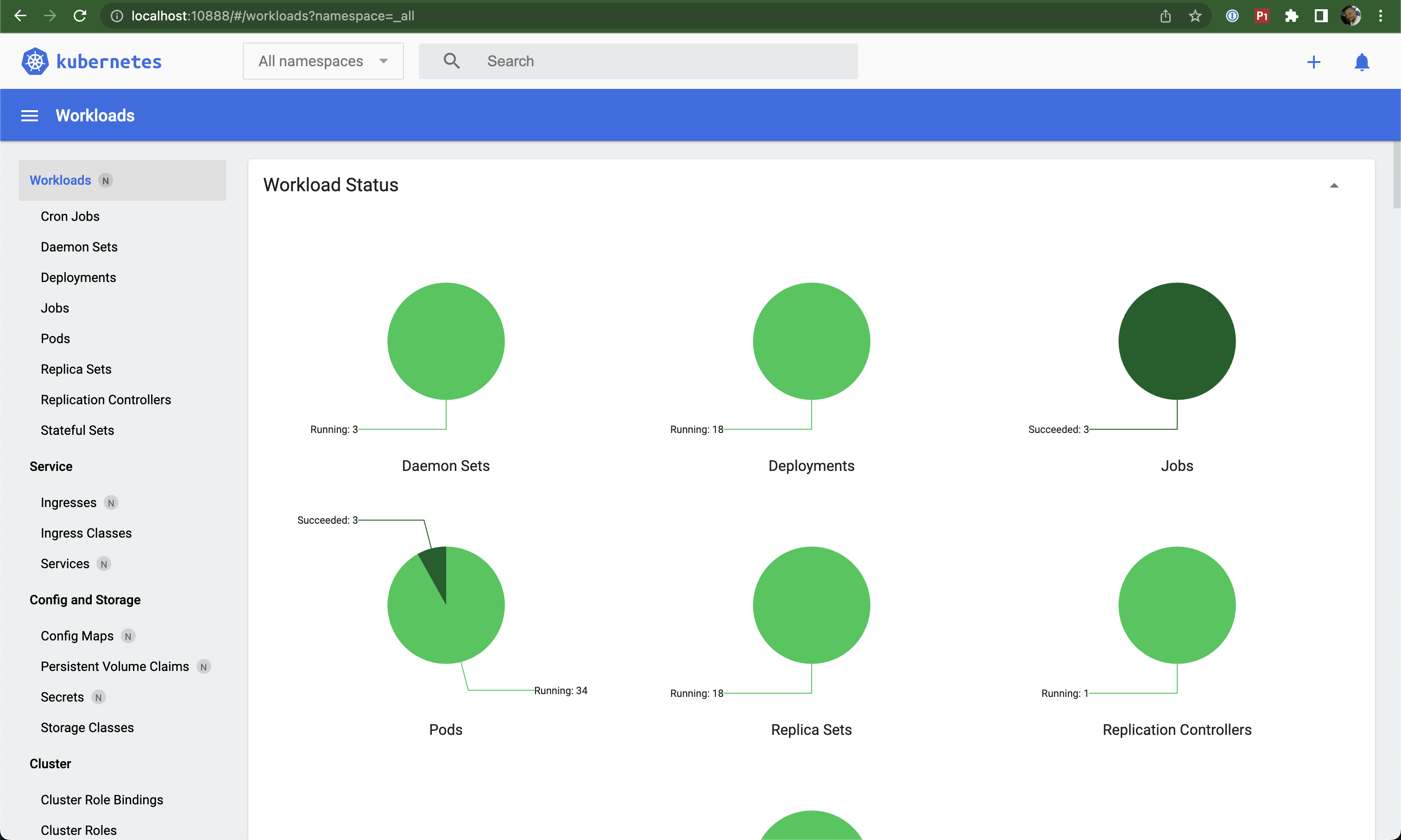
Minikube Dashboard
The Dashboard is a web-based Kubernetes user interface that lets you:
- Deploy containerized applications
- Troubleshoot applications
- Manage cluster resources
- View applications running on your cluster
- Create or modify Kubernetes resources
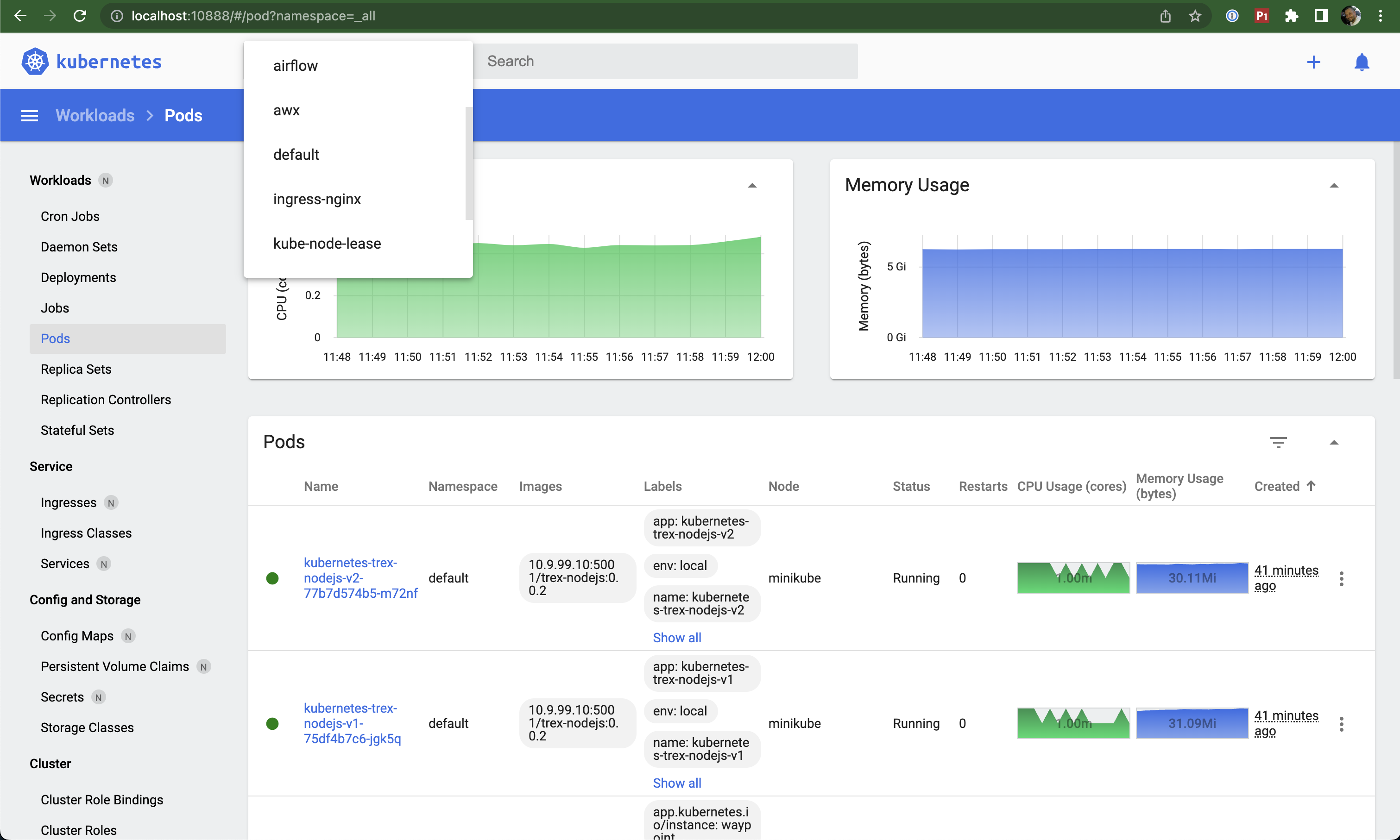
Kubernetes Pods
Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage in Kubernetes.
Key characteristics:
- Group of one or more containers
- Shared storage and network resources
- Co-located and co-scheduled
- Run in a shared context
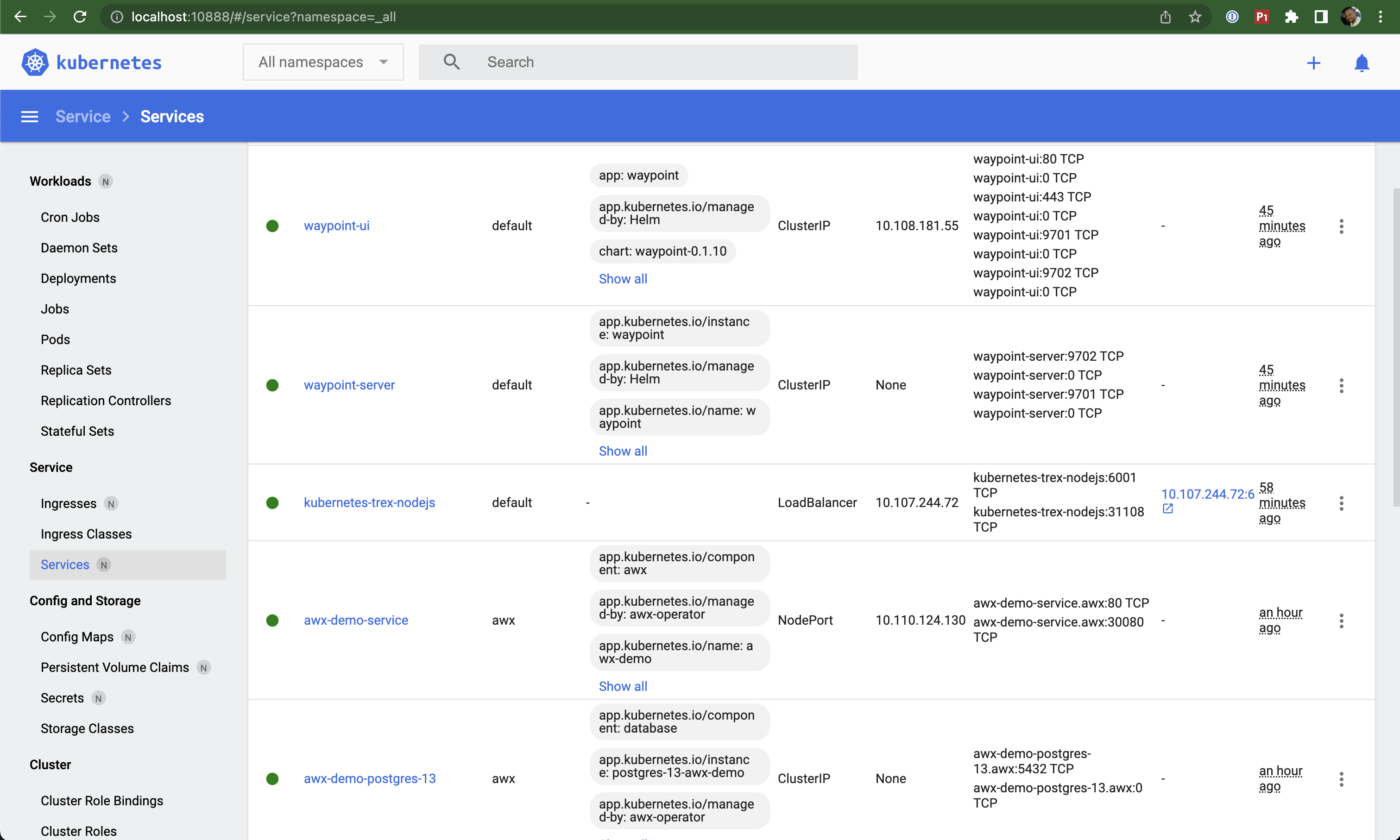
Kubernetes Services
Services are a method for exposing network applications running as Pods.
Purpose:
- Expose Pods to network traffic
- Provide stable networking for dynamic Pods
- Allow frontends to connect to backends without tracking changing IPs
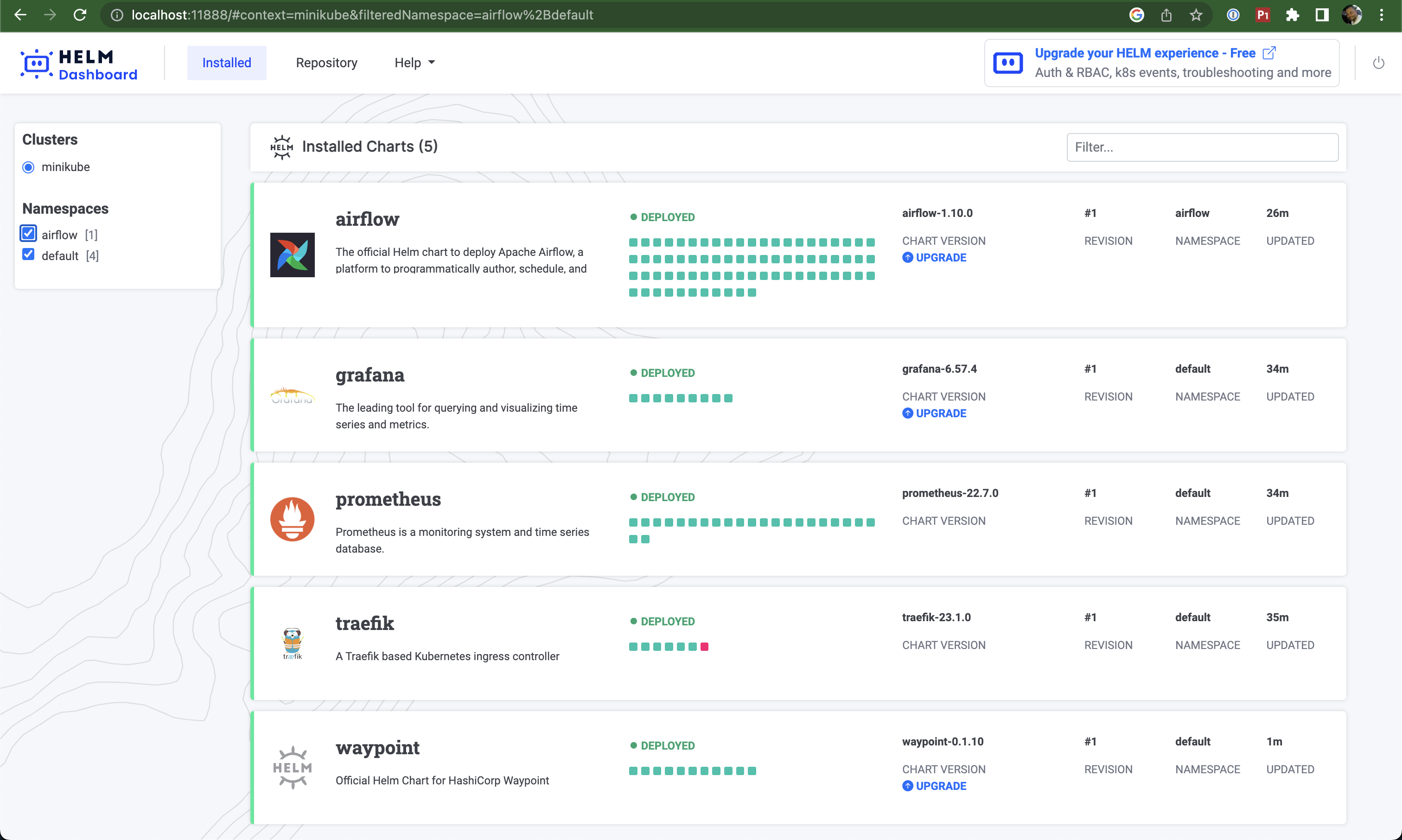
Helm Dashboard

Helm Dashboard is an open-source UI for Helm charts that allows you to:
- View installed Helm charts and their revision history
- See manifest diffs between revisions
- Browse Kubernetes resources created by charts
- Perform rollbacks or upgrades with clear manifest diffs
- Switch between multiple clusters
- Use locally or install into a Kubernetes cluster
Access URL: http://localhost:11888/
K9s CLI
K9s is a terminal-based UI for Kubernetes that wraps kubectl functionality for intuitive cluster interaction.
To launch K9s:
vagrant ssh
k9s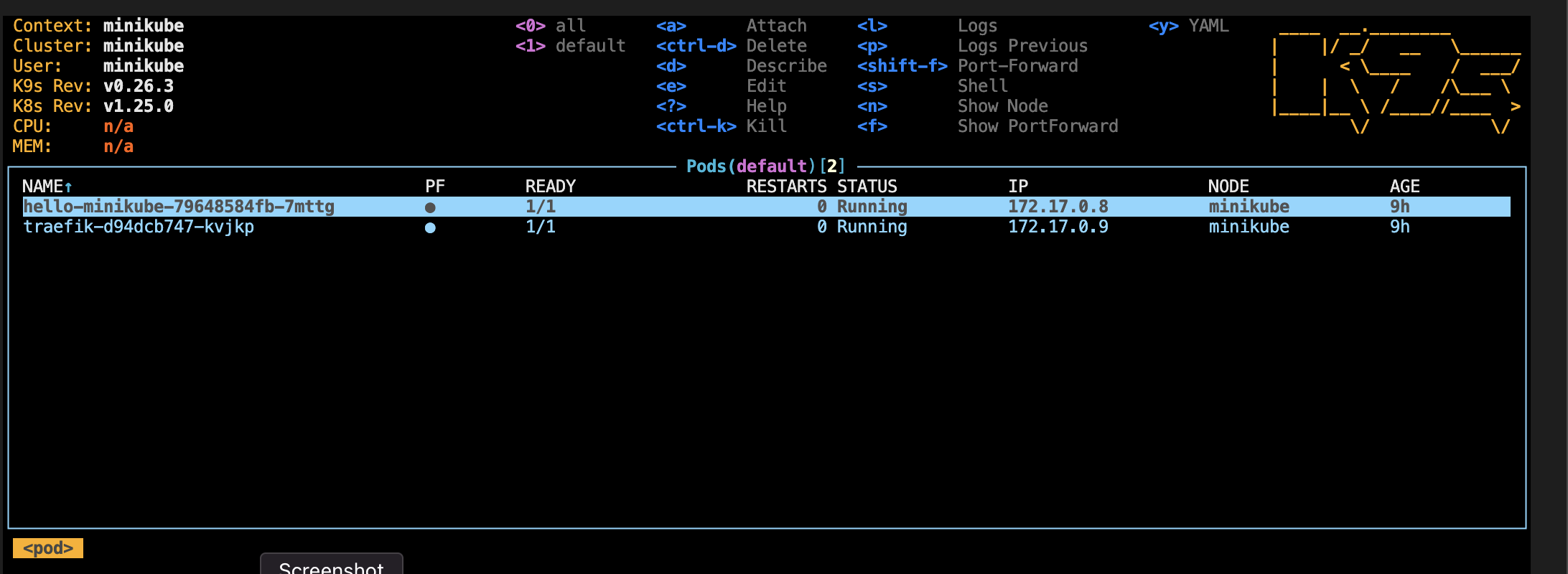
K9s Tips:
- Press
0to display all namespaces - Press
:to bring up command prompt - Navigate with arrow keys and interact using buttons shown in the top right
- Press
lto show logs of selected pod
For more information, visit the K9s website.
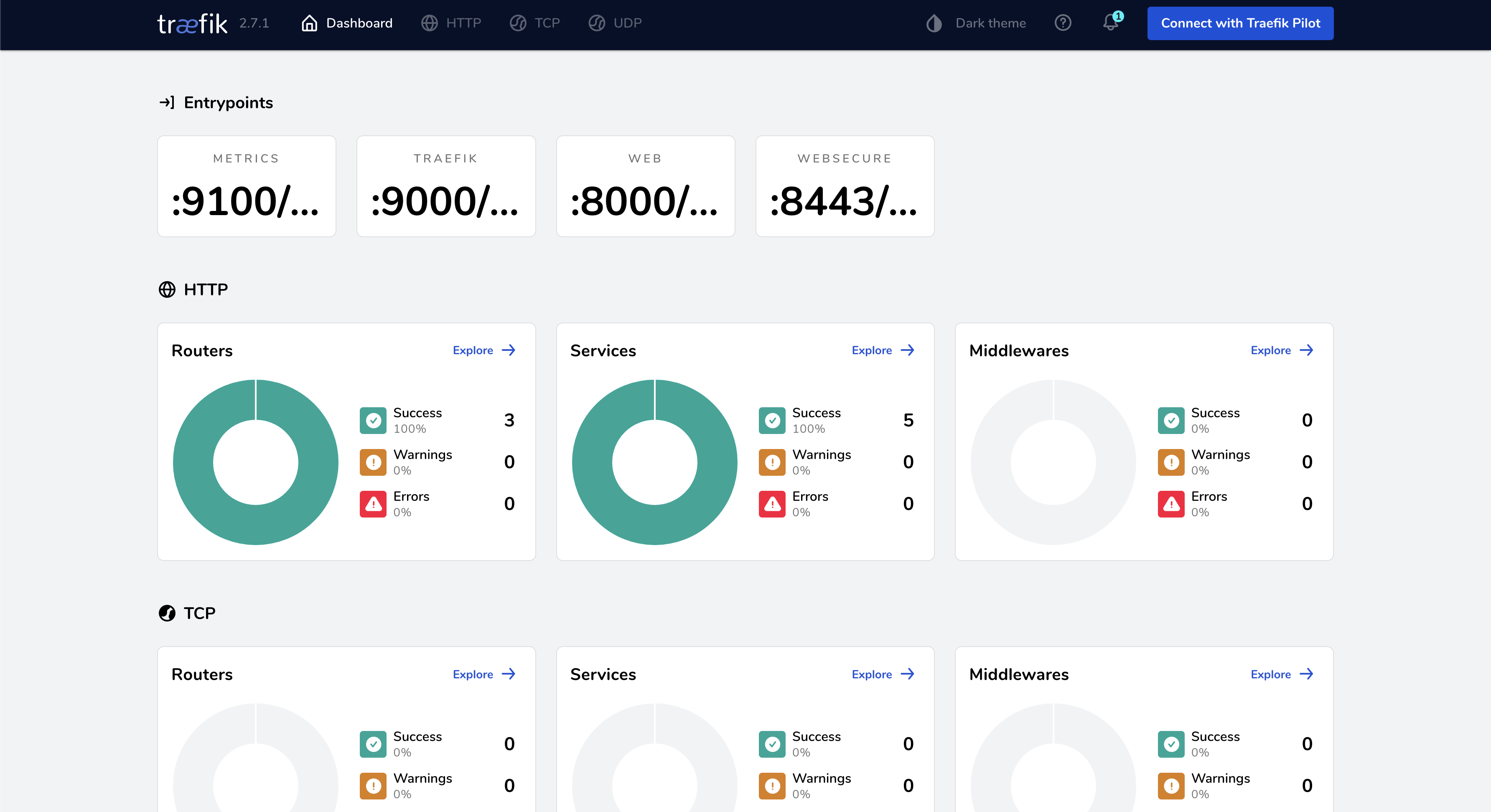
Traefik on Minikube

Traefik is a modern HTTP reverse proxy and load balancer that can be used as an Ingress controller for Kubernetes.
Access URLs:
- Dashboard: http://localhost:18181/dashboard/
- Load Balancer: http://localhost:18080
- Documentation: http://localhost:3333/#/minikube/README?id=traefik-on-minikube
🧩 kubectl Commands
You can interact with kubectl from your computer using:
vagrant ssh -c "sudo kubectl command"Common Command Examples
Get nodes:
vagrant ssh -c "sudo kubectl get nodes"Get all resources:
vagrant ssh -c "kubectl get all -A"or inside HashiQube:
kubectl get all -AGet deployments:
vagrant ssh -c "sudo kubectl get deployments"Get services:
vagrant ssh -c "sudo kubectl get services"Alternatively, SSH into the VM with vagrant ssh and then use sudo kubectl get nodes.
📚 Resources
💡 Tips for Using Minikube
- Start Simple: Begin with basic deployments and gradually add complexity
- Use the Dashboard: The Kubernetes Dashboard provides a visual way to understand your cluster
- Experiment with Services: Try different service types (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer) to understand networking
- Learn kubectl: Become familiar with common kubectl commands for managing your cluster
- Use Namespaces: Organize your resources into namespaces for better management
#!/bin/bash
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-minikube/
# https://medium.com/@wisegain/minikube-cheat-sheet-a273385e66c9
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/web-ui-dashboard/
# https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/handbook/persistent_volumes/
function minikube-install() {
# Determine CPU Architecture
arch=$(lscpu | grep "Architecture" | awk '{print $NF}')
if [[ $arch == x86_64* ]]; then
ARCH="amd64"
HELLO_MINIKUBE_IMAGE="k8s.gcr.io/echoserver:1.4"
elif [[ $arch == aarch64 ]]; then
ARCH="arm64"
# https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/issues/11107
HELLO_MINIKUBE_IMAGE="preslavmihaylov/kubehelloworld:latest"
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ CPU is $ARCH"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Docker Daemon is running (Dependency)"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if pgrep -x "dockerd" >/dev/null
then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Docker is running"
else
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Ensure Docker is running.."
sudo bash /vagrant/docker/docker.sh
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Delete K3s if exists"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo bash /usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.sh || true
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing Minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
if [ -f /usr/local/bin/minikube ]; then
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Minikube found at /usr/local/bin/minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
else
wget -q https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-$ARCH -O /tmp/minikube
sudo chmod +x /tmp/minikube
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin/
sudo install /tmp/minikube /usr/local/bin/
fi
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Delete Minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
for mkd in $(ps aux | grep -e dashboard -e kubectl | grep -v grep | grep -v nomad | tr -s " " | cut -d " " -f2); do bash -c "sudo kill -9 $mkd || true"; done
sleep 10;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Check minikube proccesses"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
bash -c "ps aux | grep -e dashboard -e kubectl || true"
sleep 5;
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube delete --all --purge
sleep 30;
sudo rm -rf /home/vagrant/.kube
sudo rm -rf /home/vagrant/.minikube
# BUG: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/issues/7511 - gave me lots of issues
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker/volumes/minikube
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant mkdir /home/vagrant/.kube
# sudo chmod -R 777 /home/vagrant/.kube
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ docker system prune -a"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
yes | sudo docker system prune -a
yes | sudo docker system prune --volumes
sudo docker volume prune -f
# BUG: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/issues/7179
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing Contrack"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo apt-get install --assume-yes conntrack ethtool socat
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Launching Minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/commands/start/
# https://unofficial-kubernetes.readthedocs.io/en/latest/admin/admission-controllers/
# https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/issues/604
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant CHANGE_MINIKUBE_NONE_USER=true minikube start --driver=docker --force-systemd=true --insecure-registry="10.9.99.0/24" --cpus=$(expr $(lscpu -p=CPU | tail -n1) + 1) --memory=$(expr $(free -m | tr -s " " | grep Mem | cut -d " " -f2) - 2048) --disk-size=2g --mount-string="/vagrant:/vagrant" --mount --extra-config=apiserver.enable-admission-plugins="DefaultStorageClass"
# --extra-config=apiserver.enable-admission-plugins="LimitRanger,NamespaceExists,NamespaceLifecycle,ResourceQuota,ServiceAccount,DefaultStorageClass,MutatingAdmissionWebhook"
# "ResourceQuota,ServiceAccount,MutatingAdmissionWebhook,LimitRanger,NamespaceExists,NamespaceLifecycle," --kubelet.node-ip=10.9.99.10 --apiserver-name=0.0.0.0 --apiserver-ips=0.0.0.0
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant curl -sLO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/$ARCH/kubectl
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant chmod +x kubectl
sudo install kubectl /usr/local/bin/
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing k8s CLI"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo curl -sS https://webinstall.dev/k9s | bash
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Initially, some services such as the storage-provisioner, may not yet be in a Running state. This is a normal condition during cluster bring-up, and will resolve itself momentarily. For additional insight into your cluster state, minikube bundles the Kubernetes Dashboard, allowing you to get easily acclimated to your new environment:\nSleep 30s.."
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sleep 30;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Get minikube IP"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
MINIKUBE_IP=$(sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube ip)
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube ip
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Enable Minikube Ingress Addon"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons enable ingress
# # Docker Registry via Minikube
# # https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/handbook/registry/
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Enable Minikube Docker Registry Addon"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons enable registry
# sleep 30;
# attempts=0
# max_attempts=15
# while ! ( sudo netstat -nlp | grep 5001 ) && (( $attempts < $max_attempts )); do
# attempts=$((attempts+1))
# sleep 10;
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/registry 5001:80 --address=\"0.0.0.0\", (${attempts}/${max_attempts}) sleep 10s"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/registry 5001:80 --address="0.0.0.0" > /dev/null 2>&1 &
# done
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Enable Minikube Default Storage Class Addon"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons enable default-storageclass
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Enable Minikube Storage Provisioner Addon"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons enable storage-provisioner
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Enable Minikube Metrics-Server Addon"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons enable metrics-server
# https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/commands/dashboard/
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Starting Minikube dashboard"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant nohup minikube dashboard --url &
sleep 30;
# via port-forward
attempts=0
max_attempts=15
while ! ( sudo netstat -nlp | grep 10888 ) && (( $attempts < $max_attempts )); do
attempts=$((attempts+1))
sleep 10;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward -n kubernetes-dashboard service/kubernetes-dashboard 10888:80 --address=\"0.0.0.0\", (${attempts}/${max_attempts}) sleep 10s"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl port-forward -n kubernetes-dashboard service/kubernetes-dashboard 10888:80 --address="0.0.0.0" > /dev/null 2>&1 &
done
# via kube proxy
#sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant nohup kubectl proxy --address="0.0.0.0" -p 10888 --disable-filter=true --accept-hosts='^*$' &
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Tada! Minikube Dashboard is now available at http://localhost:10888"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sleep 10;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ sudo minikube status"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube status
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ sudo minikube service list"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube service list
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ sudo kubectl get nodes"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl get nodes
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Interact with Minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ vagrant kubectl get po -A"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl get po -A
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ minikube kubectl -- get po -A"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube kubectl -- get po -A
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Start Minikube Tunnel"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube tunnel > /dev/null 2>&1 &
# Disable hello-minikube workload, has trouble starting up
# # https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/hello-minikube/
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Deploy hello-minikube application"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Create a sample deployment and expose it on port 3000:"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl create deployment hello-minikube --image=$HELLO_MINIKUBE_IMAGE"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl expose deployment hello-minikube --type=NodePort --port=3000"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl create deployment hello-minikube --image=$HELLO_MINIKUBE_IMAGE
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl expose deployment hello-minikube --type=NodePort --port=3000
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ It may take a moment, but your deployment will soon show up when you run:"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl get services hello-minikube"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sleep 15;
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl get services hello-minikube
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ The easiest way to access this service is to let kubectl to forward the port:"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward service/hello-minikube 18888:3000"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sleep 25;
# attempts=0
# max_attempts=15
# while ! ( sudo netstat -nlp | grep 18888 ) && (( $attempts < $max_attempts )); do
# attempts=$((attempts+1))
# sleep 10;
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward -n default service/hello-minikube 18888:3000 --address=\"0.0.0.0\", (${attempts}/${max_attempts}) sleep 10s"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl port-forward -n default service/hello-minikube 18888:3000 --address="0.0.0.0" > /dev/null 2>&1 &
# done
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Browse the catalog of easily installed Kubernetes services:"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ minikube addons list"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant minikube addons list
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Get all Pods and Services"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl get pod,svc -A"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl get pod,svc -A
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"View Minikube Config"
# echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"kubectl config view"
# sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl config view
# TODO: uplift below, see issues in hashiqube
# https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/#from-script
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Helm not installed, installing.."
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
cd /tmp
sudo curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3
sudo chmod 700 get_helm.sh
sudo /tmp/get_helm.sh
cd ~/
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm version"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm version
#https://helm.sh/docs/intro/quickstart/#initialize-a-helm-chart-repository
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Helm add Bitnami repo"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm repo update"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm repo update
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm search repo bitnami"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm search repo bitnami
# https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/getting-started/install-traefik/
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing Traefik using Helm Chart"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm repo add traefik https://helm.traefik.io/traefik"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm repo add traefik https://helm.traefik.io/traefik
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm repo update
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ helm install traefik traefik/traefik"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm install traefik traefik/traefik
sleep 30;
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward 18181:9000"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl port-forward $(kubectl get pods --selector "app.kubernetes.io/name=traefik" --output=name) 18181:9000 --address="0.0.0.0" > /dev/null 2>&1 &
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl port-forward 18080:9000"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl port-forward $(kubectl get pods --selector "app.kubernetes.io/name=traefik" --output=name) 18080:9000 --address="0.0.0.0" > /dev/null 2>&1 &
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Get all Pods and Services"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ kubectl get pod,svc -A"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant kubectl get pod,svc -A
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Docker stats"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant docker stats --no-stream -a
# https://github.com/komodorio/helm-dashboard
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Installing Helm Dashboard"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm plugin install https://github.com/komodorio/helm-dashboard.git
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Running Helm Dashboard"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
sudo --preserve-env=PATH -u vagrant helm dashboard --bind=0.0.0.0 --port 11888 --no-browser --no-analytics > /dev/null 2>&1 &
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Minikube Dashboard: http://localhost:10888"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Minikube Documentation: http://localhost:3333/#/minikube/README"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Helm Dashboard: http://localhost:11888"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Helm Dashboard Documentation: http://localhost:3333/#/minikube/README?id=helm-dashboard-by-komodor"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Traefik Dashboard: http://localhost:18181/dashboard/"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Traefik Loadbalancer: http://localhost:18080"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ Traefik Documentation: http://localhost:3333/#/minikube/README?id=traefik-on-minikube"
echo -e '\e[38;5;198m'"++++ "
}
minikube-install




